
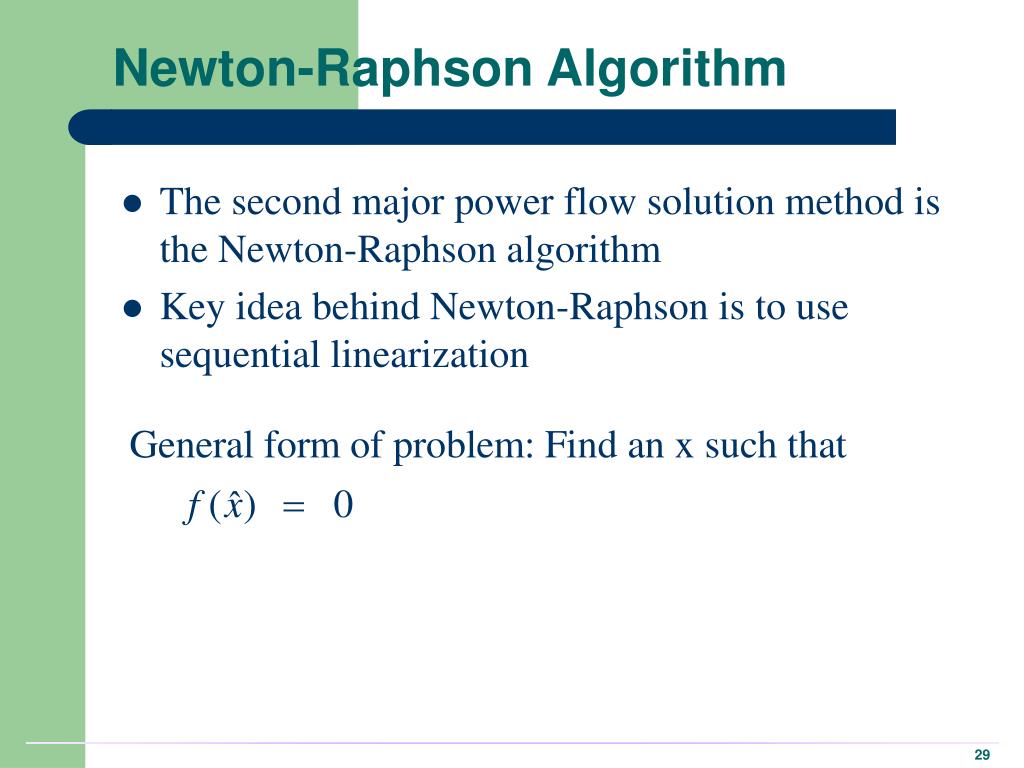
- #Newton raphson method power flow expected value generator#
- #Newton raphson method power flow expected value plus#
The elements of the tree are known as branches. Tree is a subgraph containing all the nodes of the original graph but no closed path.General equation for n-bus network based on Kirchhoff’s current law and admittance form is = * where is the n-bus current matrix, is the n-bus voltage matrix and is called the bus-admittance matrix and above equation is written as I = Y bus V
#Newton raphson method power flow expected value plus#
One of the generation bus is selected as slack bus and the generators at this bus supply the difference between the specified real power injected into the system at other buses and the total output of the system plus system power losses.Īns. What are the guidelines for choosing slack bus ?Īns. The need to designate one of the buses as a slack bus is obviously due to the fact that the system power losses are not known initially and, therefore, the net power flow into the system cannot be fixed in advance.Ĩ. What is necessity of designating one of the bus as a slack bus ?Īns. At this bus, the magnitude and phase angle of the voltage are specified and the active and reactive powers are to be determined through the solution of the equations.ħ. This bus is called the slack or swing bus.
#Newton raphson method power flow expected value generator#
Because of this, one of the generator buses is made to take the additional power to supply transmission losses. The losses remain unknown until the load flow solution is complete. For these buses, we have to specify real power P injections, which is positive for generator buses and negative for load buses. In a power system, there are mainly two types of buses viz. Why is one of the buses taken as slack bus in load flow studies ?Īns. There can be more than one slack bus in a given network.Ħ. If slack bus is not specified, the generation bus usually with maximum active power P is taken as reference bus. The generators at the swing bus supply the difference of the specified active power to be injected into the system at other buses and the total system output plus losses. The difference between the expected and solved output (MW) represents the error in the prior estimate of system I 2R losses. At the swing bus, it is customary to regard the active power as unknown. Therefore, the total injected power cannot be specified at every single bus. The swing bus is a fictitious concept in load flow studies and arises because the I 2R losses of the system are not known precisely in advance for the load flow calculations. The active and reactive powers at this bus are to be determined through the solution of equations. The phase angle of the voltage is usually set equal to zero. At this bus, the magnitude and phase angle of the voltage are specified. One of the generation buses in a power system is chosen as slack or swing bus. The reactive power generation Q and phase angle δ of the voltage are to be computed. Voltage magnitude is maintained constant at a specified value by injection of reactive power. This is also called the P-V bus, and on this bus the voltage magnitude corresponding to generation voltage and true or active power P corresponding to its ratings are specified. Distinguish between voltage control bus and swing bus.Īns. The unknown quantities are active and reactive power flows.ĥ. At a reference bus, the magnitude and phase angle of the voltage are specified. Mention the items specified and not specified at a reference bus.Īns. At a generator bus voltage magnitude and true or active power are specified.Ĥ. What are quantities specified at a generator bus ?Īns. Generation or voltage-controlled or P-V buses,ģ.Depending upon which quantities have been specified, the buses are classified into following three categories Power flow analysis provides a systematic mathematical approach for determination of various bus voltages, their phase angles, active and reactive power flows through different branches, generators and loads under steady state conditions.Īns.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
